Understanding Air Cooled Condensing Units
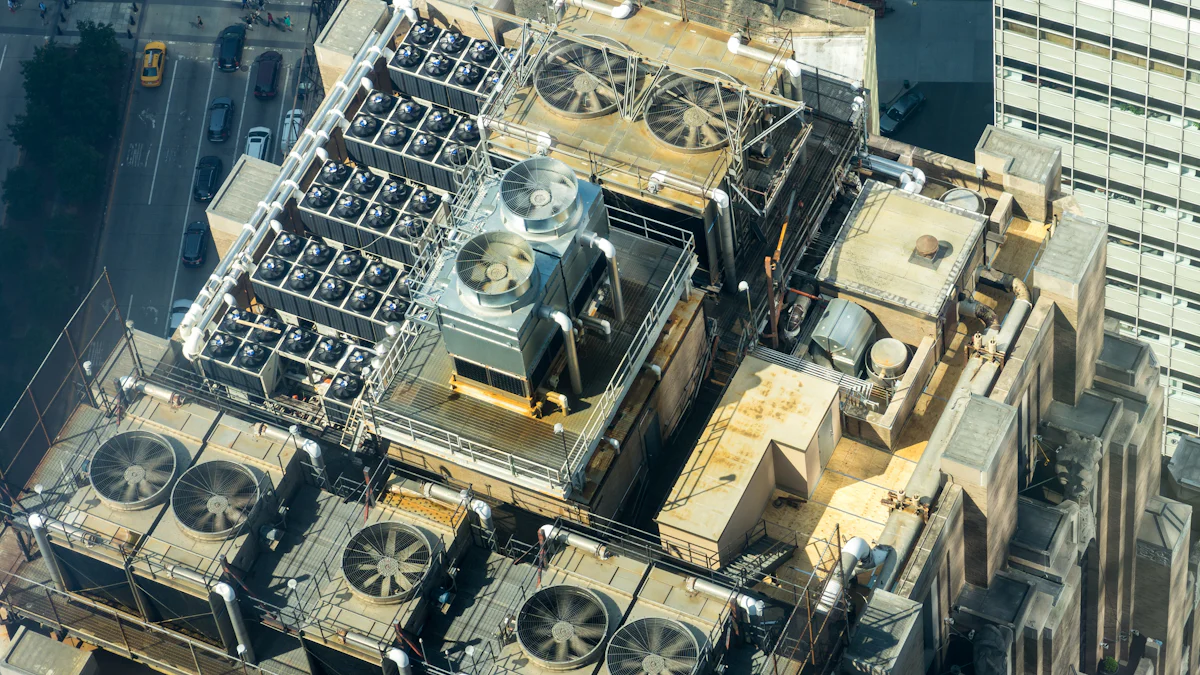
An air cooled condensing unit plays a crucial role in HVAC systems. It efficiently transfers heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding air, ensuring effective cooling. These units are designed to minimise energy consumption while providing flexibility in installation. They suit both commercial and residential buildings, offering a reliable solution for long-term use. Their design allows for less maintenance compared to water-cooled systems, making them a preferred choice for many applications.
How Air Cooled Condensing Units Work
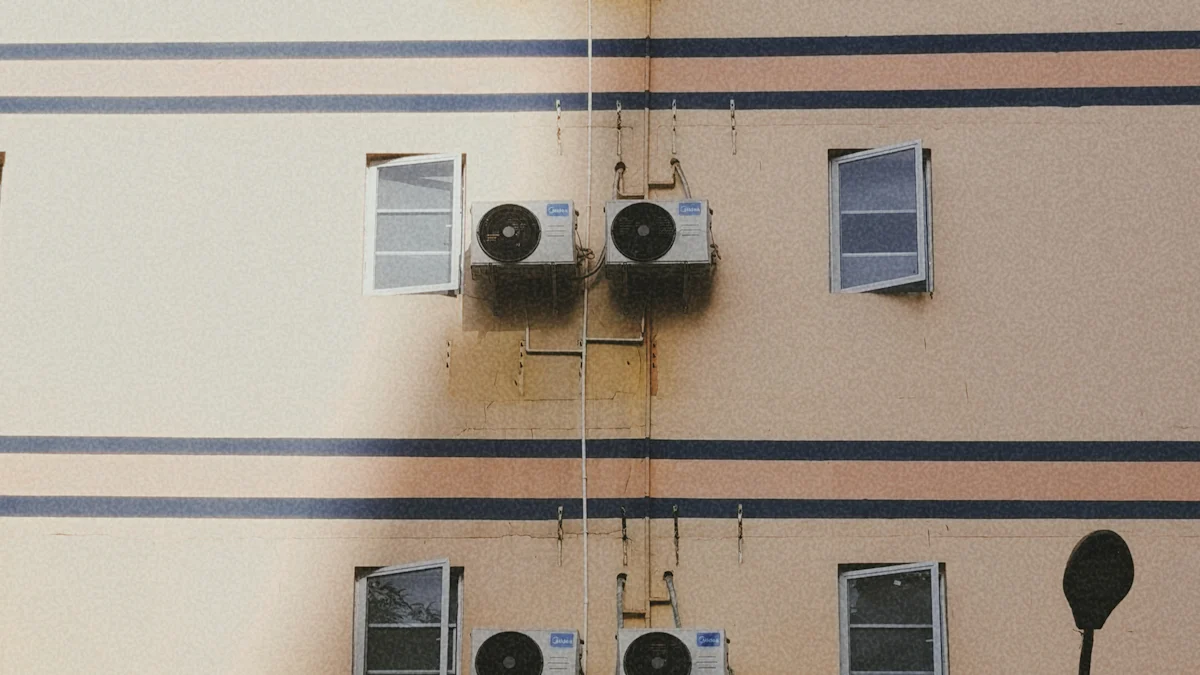

Basic Operating Principles
An Air Cooled Condensing Unit operates by efficiently transferring heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding air. The process begins when the refrigerant absorbs heat from the system, transforming into a gas. This gas then flows into the condenser coils. A fan blows air across these coils, cooling the refrigerant and causing it to condense into a liquid state. This liquid refrigerant returns to the evaporator for further cooling. Typically installed outdoors, these units ensure proper airflow and efficient cooling.
Key Components
An Air Cooled Condensing Unit comprises several essential components:
Compressor: This component compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature before it enters the condenser coils.
Condenser Coils: These coils facilitate the heat exchange process. The refrigerant releases its heat to the surrounding air, aided by the fan.
Fan: Positioned to blow air over the condenser coils, the fan plays a crucial role in cooling the refrigerant.
Controls: These include various sensors and switches that regulate the unit's operation, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
These components work together to provide a cost-effective and reliable cooling solution. The design of these units allows them to operate at low pressure, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from commercial refrigeration to industrial cooling systems.
Types of Compressors Used in Air Cooled Condensing Units
Air cooled condensing units rely on different types of compressors to function effectively. Each compressor type offers unique advantages, making them suitable for various applications. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right unit for specific needs.
Reciprocating Compressors
Reciprocating compressors operate using a piston mechanism. They compress refrigerant by drawing it into a cylinder and then pushing it out under high pressure. This type of compressor is known for its durability and reliability. It suits applications requiring high pressure and moderate capacity. Facilities management professionals often choose reciprocating compressors for their cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance. These compressors are ideal for small-scale air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
Scroll Compressors
Scroll compressors use two interleaved spiral scrolls to compress refrigerant. One scroll remains stationary while the other orbits around it, trapping and compressing the refrigerant. This design results in fewer moving parts, reducing the likelihood of mechanical failure. Scroll compressors are quieter and more energy-efficient compared to reciprocating compressors. They are preferred in environments where noise reduction and energy efficiency are priorities. Their compact size makes them suitable for residential and commercial applications.
Screw Compressors
Screw compressors utilise two helical rotors to compress refrigerant. As the rotors turn, they trap and compress the refrigerant between them. This type of compressor provides a continuous flow of refrigerant, making it highly efficient for large-scale applications. Screw compressors are known for their high cooling capacity and energy efficiency. They are often used in industrial settings where large volumes of refrigerant need to be compressed. The robust design of screw compressors ensures long-term reliability and performance.
Scientific Research Findings: Studies highlight that variable speed compressors, including screw compressors, enhance energy efficiency by adjusting speed according to cooling demand. This adaptability contributes to the overall efficiency of air cooled condensing units.
Applications of Air Cooled Condensing Units

Commercial Refrigeration
Air cooled condensing units find extensive use in commercial refrigeration. They provide efficient cooling solutions for supermarkets, hypermarkets, and cold storage warehouses. These units help maintain optimal temperatures for perishable goods, ensuring food safety and quality. Their design allows for easy installation and maintenance, making them a cost-effective choice for businesses. Hotels and restaurants also benefit from these units, as they support refrigeration needs in commercial kitchens and food storage areas.
Air Conditioning Systems
In air conditioning systems, air cooled condensing units offer reliable cooling for both residential and commercial buildings. They are particularly suitable for small-scale air conditioning applications where water-cooled systems are impractical. These units serve as an ideal solution for decentralised cooling demands, providing flexibility in installation. Facilities such as data centres and laboratories rely on air cooled condensing units to maintain controlled environments, ensuring the smooth operation of sensitive equipment.
Industrial Applications
Industries utilise air cooled condensing units for various applications. Factories, petrochemical plants, and power plants benefit from their robust design and high cooling capacity. These units support processes that require consistent temperature control, such as chemical manufacturing and ice production. In regions with water scarcity, air cooled condensing units serve as an alternative to water-cooled systems, offering efficient cooling without the need for a water supply. Their adaptability makes them a valuable asset in diverse industrial settings.
Benefits of Air Cooled Condensing Units
Energy Efficiency
Air Cooled Condensing Units excel in energy efficiency, making them a preferred choice for many applications. They utilise ambient air to dissipate heat from the refrigerant, which reduces the need for additional energy sources. This method of heat transfer ensures that these units consume less energy compared to other cooling systems. By operating efficiently, they contribute to creating comfortable environments while promoting energy conservation. The design of these units allows them to adjust their cooling capacity based on demand, further enhancing their energy-saving capabilities. This adaptability not only lowers operational costs but also supports environmental sustainability.
Installation and Maintenance
The installation and maintenance of Air Cooled Condensing Units are straightforward and cost-effective. Their design eliminates the need for a water supply, simplifying the installation process and reducing associated costs. These units can be placed outdoors, which saves valuable indoor space and allows for flexible placement options. Maintenance requirements are minimal due to their robust construction and fewer moving parts. Regular checks and cleaning of components such as fans and coils ensure optimal performance. This ease of maintenance translates to lower long-term costs and less downtime, making them an attractive option for both commercial and residential settings.
Considerations for Choosing an Air Cooled Condensing Unit
Selecting the right Air Cooled Condensing Unit involves evaluating several factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. These considerations help in making informed decisions that align with specific cooling needs and environmental conditions.
Climate and Environmental Factors
Climate plays a significant role in determining the suitability of an Air Cooled Condensing Unit. In regions with high ambient temperatures, units with enhanced cooling capacities are essential to maintain efficiency. The unit's ability to dissipate heat effectively depends on the surrounding air temperature. Therefore, understanding local climate conditions helps in choosing a unit that can perform reliably under varying weather patterns.
Environmental factors such as humidity and air quality also influence the choice of condensing units. High humidity levels can affect the unit's efficiency, requiring models designed to handle such conditions. Additionally, areas with poor air quality may necessitate units with robust filtration systems to prevent dust and debris from affecting performance.
Space and Location Constraints
Space availability and location constraints are crucial when selecting an Air Cooled Condensing Unit. These units require adequate space for installation to ensure proper airflow and maintenance access. Limited space may restrict the size and type of unit that can be installed, necessitating compact models that still deliver the required cooling capacity.
The location of the unit impacts its efficiency and noise levels. Units placed too close to walls or other structures may experience restricted airflow, reducing their effectiveness. It is important to consider noise levels, especially in residential or noise-sensitive areas. Choosing a unit with low sound emissions ensures minimal disturbance to occupants and neighbours.
HVAC experts emphasise the importance of considering factors such as cooling capacity, energy efficiency, and noise levels when selecting an air-cooled condensing unit. These elements ensure that the chosen unit meets the specific requirements of the environment and application.
Air Cooled Condensing Units offer numerous benefits, including energy efficiency and ease of maintenance. They provide a cost-effective solution for various applications, from residential to industrial settings. When selecting a unit, one must consider factors such as climate conditions and space constraints. These considerations ensure optimal performance and longevity. Exploring specific models and applications can further enhance understanding and decision-making. By choosing energy-efficient units, individuals contribute to reducing environmental impact and operational costs, aligning with ethical considerations for sustainable practices.
See Also
A Comprehensive Guide To Water Chiller Units
An Overview Of The ARKREF CO₂ Refrigeration System
The Advantages Of CO₂ Transcritical Refrigeration Systems
The Superiority Of CO₂ Cascade Refrigeration Units
Delving Into ARKREF's CO₂ Transcritical Refrigeration Technology

